

Unlike hyperkalemia, these additional changes are not related to the degree of hypokalemia.ĮCG signs of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia may not be obvious even in patients who have deranged plasma calcium concentrations that are clinically significant. The ST segment may become depressed and the T wave inverted. With hypokalemia, the T wave becomes flattened together with appearance of a prominent U wave. The patient ’s presenting history and physical findings would help to differentiate the two.) (NB: The narrow and tall peaked T wave of hyperkalemia may be confused with the hyper-acute T wave occasionally seen in transmural myocardial infarction. If the rise in serum potassium continues unabated, the heart arrests in asystole.
#Hyperkalemia ecg changes series#
When hyperkalemia is very severe, the widened QRS complexes merge with their corresponding T waves and the resultant ECG looks like a series of sine waves (C). Hyperkalemia should be suspect if these limits are exceeded in more than one lead.Īs serum potassium concentration continues to rise, the PR interval becomes longer, the P wave loses its amplitude and may disappear, and the QRS complex widens (B). It is unusual for T waves to be taller than 5 mm in limb leads and taller than 10 mm in chest leads. Narrow and tall peaked T wave (A) is an early sign of hyperkalemia.
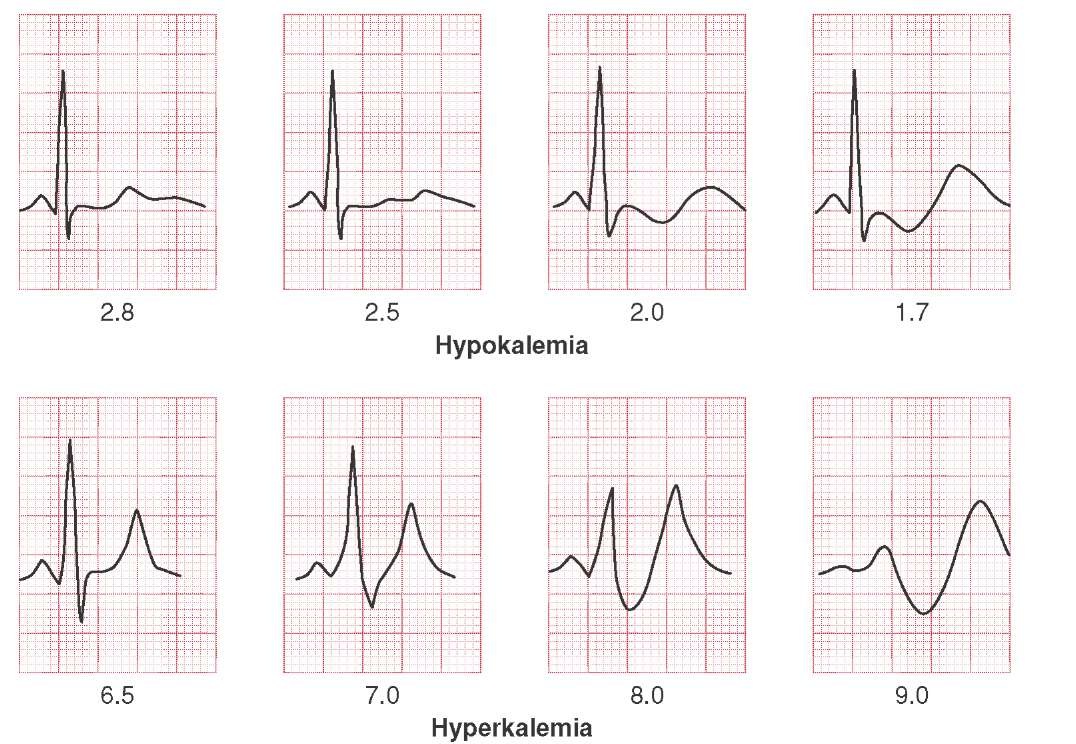
Hence its serum concentration has a profound effect on the QRS and ST-T complex. Serum potassium is the major intracellular ion that participates in the depolarization and repolarization of myocardial cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
